Here are some of the examples based on speedup and Amdahl's law. The purpose of these examples is to understand the concepts by applying them in given situations.
Example 1:
A computer spends 80 percent of time executing a particular type of instruction. Engineers claim to improve that instruction execution by the factor of 10. What is the resultant speedup obtained?
Sol:
We need to apply Amdahl's law here.

Example 2:
A computer program to be executed by a given processor has the following characteristic:
The processor is clocked at 2GHz.
Calculate the speedup obtained in each of the cases
1. Branch instruction CPI is changed from 4 to 3
2. Clock frequency is changed from 2GHz to 2.3GHz
3. Store instruction CPI is changed from 3 to 2.
Sol.
Let us discuss each case one by one.
Case1: Branch instruction CPI is changed from 4 to 3

Here Frac_used=0.2 (from table given in the table)
Speedup_used= 4/3=1.33
Frac_unused= 1- Frac_used= 0.8
Case2: Clock frequency is changed from 2GHz to 2.3GHz

execution time is inversely proportional to the frequency with which the processor is operating.

Frac_used=0.1 (from the table given in the question)
speedup_used= 3/2=1.5
Frac_unused= 1- Frac_used=0.9
Example 1:
A computer spends 80 percent of time executing a particular type of instruction. Engineers claim to improve that instruction execution by the factor of 10. What is the resultant speedup obtained?
Sol:
We need to apply Amdahl's law here.

Example 2:
A computer program to be executed by a given processor has the following characteristic:
S.No
|
Instruction type
|
% of time
|
CPI
|
1
|
Integer-type
|
40
|
1
|
2
|
Branch
|
20
|
4
|
3
|
Load
|
30
|
2
|
4
|
Store
|
10
|
3
|
Calculate the speedup obtained in each of the cases
1. Branch instruction CPI is changed from 4 to 3
2. Clock frequency is changed from 2GHz to 2.3GHz
3. Store instruction CPI is changed from 3 to 2.
Sol.
Let us discuss each case one by one.
Case1: Branch instruction CPI is changed from 4 to 3

Here Frac_used=0.2 (from table given in the table)
Speedup_used= 4/3=1.33
Frac_unused= 1- Frac_used= 0.8
Case2: Clock frequency is changed from 2GHz to 2.3GHz

execution time is inversely proportional to the frequency with which the processor is operating.

Frac_used=0.1 (from the table given in the question)
speedup_used= 3/2=1.5
Frac_unused= 1- Frac_used=0.9



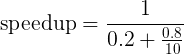












No comments:
Post a Comment